google-cloud-cpp
HOWTO: Google Cloud C++ Client Library + Cloud Trace integration.
This directory contains a small example showing how to enable OpenTelemetry tracing for a Google Cloud Storage (GCS) client. The traces are collected and sent to Cloud Trace.
This quickstart assumes the reader is familiar with how to build and use the GCS client. If not, see the GCS quickstart.
The quickstart also assumes the reader is familiar with how to build the Cloud Trace C++ client library. If not, see the Cloud Trace quickstart. Note, for example, that the Cloud Trace Exporter requires dependencies on gRPC and Protobuf, which the GCS client does not.
The Quickstart
What it does
The quickstart installs a Cloud Trace exporter. It creates a GCS client, with tracing enabled. The client makes some routine calls, each of which are traced. Upon exit of the quickstart, the collected traces are sent to Cloud Trace.
Viewing the trace in Cloud Trace
To find the traces created by this quickstart, we can follow the documentation
to Find and explore traces. We can open the Cloud Trace UI in the Google Cloud
project we supplied to the quickstart. We can search using the filter
SpanName:storage::Client to find any spans created by the GCS client.
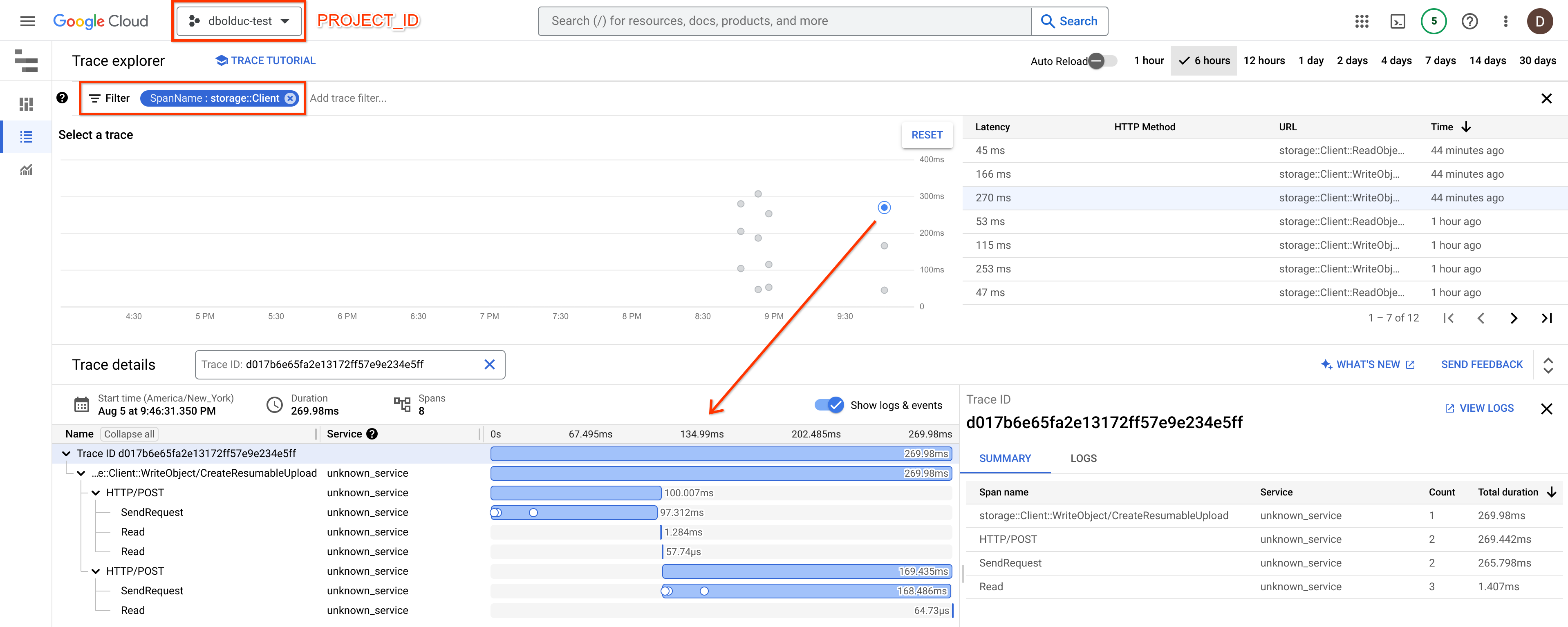
For an overview of the Cloud Trace UI, see: Find and explore traces.
OpenTelemetry Dependency
The Google Cloud C++ client libraries use OpenTelemetry to provide
observability into their operation at runtime. To enable tracing,
google-cloud-cpp takes a direct dependency on
opentelemetry-cpp.
OpenTelemetry provides full install instructions. We will highlight the important points.
Compatibility with Abseil
OpenTelemetry vendors-in Abseil types, defining them in namespace absl. The
Google Cloud client libraries depends on Abseil, which also defines these types
in the same namespace. In order to avoid ambiguous symbols, we must set certain
flags when compiling opentelemetry-cpp.
Using with Bazel
:warning: If you are using Windows or macOS there are additional instructions at the end of this document.
-
Install Bazel using the instructions from the
bazel.buildwebsite. -
Compile this example using Bazel:
cd $HOME/google-cloud-cpp/google/cloud/opentelemetry/quickstart bazel build ...Note that Bazel automatically downloads and compiles all dependencies of the project. As it is often the case with C++ libraries, compiling these dependencies may take several minutes.
-
Run the example, changing the placeholders to appropriate values:
bazel run :quickstart -- [BUCKET_NAME] [PROJECT_ID]
Details
Note the following feature flag explicitly set in the .bazelrc. This flag
enables OpenTelemetry tracing instrumentation in google-cloud-cpp.
# Enables tracing instrumentation in google-cloud-cpp
build --@google_cloud_cpp//:enable_opentelemetry
If you are using an OpenTelemetry version < v1.16.0, you must also supply the
following flag for compatibility with Abseil. Without this flag, the above
bazel build ... command will fail.
build --@io_opentelemetry_cpp//api:with_abseil
Also note that we explicitly load OpenTelemetry’s dependencies in the
WORKSPACE.bazel.
Using with CMake
:warning: If you are using Windows or macOS there are additional instructions at the end of this document.
Building from Source
Building google-cloud-cpp
The packaging guide contains instructions for how to build from source.
The Google Cloud exporters are built as part of the opentelemetry feature.
This quickstart also uses the GCS client, from the storage feature.
To enable these features, add the following to your CMake configuration command:
-DGOOGLE_CLOUD_CPP_ENABLE="storage,opentelemetry"
Details
We must supply the -DWITH_ABSEIL=ON flag when compiling opentelemetry-cpp
for compatibility with Abseil.
We must also ensure that the -DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD used to compile
opentelemetry-cpp matches the language standard used to compile abseil-cpp.
OpenTelemetry defaults the language standard if it is not explicitly set. So it is good practice to explicitly set the language standard.
While OpenTelemetry supports C++>=11, google-cloud-cpp requires C++>=14. So
you can use -DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=14, -DCMAKE_CXX_STANDARD=17, or higher.
Package Managers
vcpkg
-
Install the dependencies for this quickstart:
cd $HOME/vcpkg ./vcpkg install google-cloud-cpp[core,opentelemetry,storage]Note that, as it is often the case with C++ libraries, compiling these dependencies may take several minutes.
-
Configure CMake:
cd $HOME/google-cloud-cpp/google/cloud/opentelemetry/quickstart cmake -S . -B .build -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=$HOME/vcpkg/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake cmake --build .build -
Run the example, changing the placeholder(s) to appropriate values:
.build/quickstart [BUCKET_NAME] [PROJECT_ID]
Other
We are working on this, but at the moment, no other package managers support
google-cloud-cpp’s native integration with Cloud Trace.
Platform Specific Notes
macOS
gRPC requires an environment variable to configure the trust store for SSL certificates, you can download and configure this using:
curl -Lo roots.pem https://pki.google.com/roots.pem
export GRPC_DEFAULT_SSL_ROOTS_FILE_PATH="$PWD/roots.pem"
Windows
Bazel tends to create very long file names and paths. You may need to use a
short directory to store the build output, such as c:\b, and instruct Bazel to
use it via:
bazel --output_user_root=c:\b build ...
gRPC requires an environment variable to configure the trust store for SSL certificates, you can download and configure this using:
@powershell -NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy unrestricted -Command ^
(new-object System.Net.WebClient).Downloadfile( ^
'https://pki.google.com/roots.pem', 'roots.pem')
set GRPC_DEFAULT_SSL_ROOTS_FILE_PATH=%cd%\roots.pem